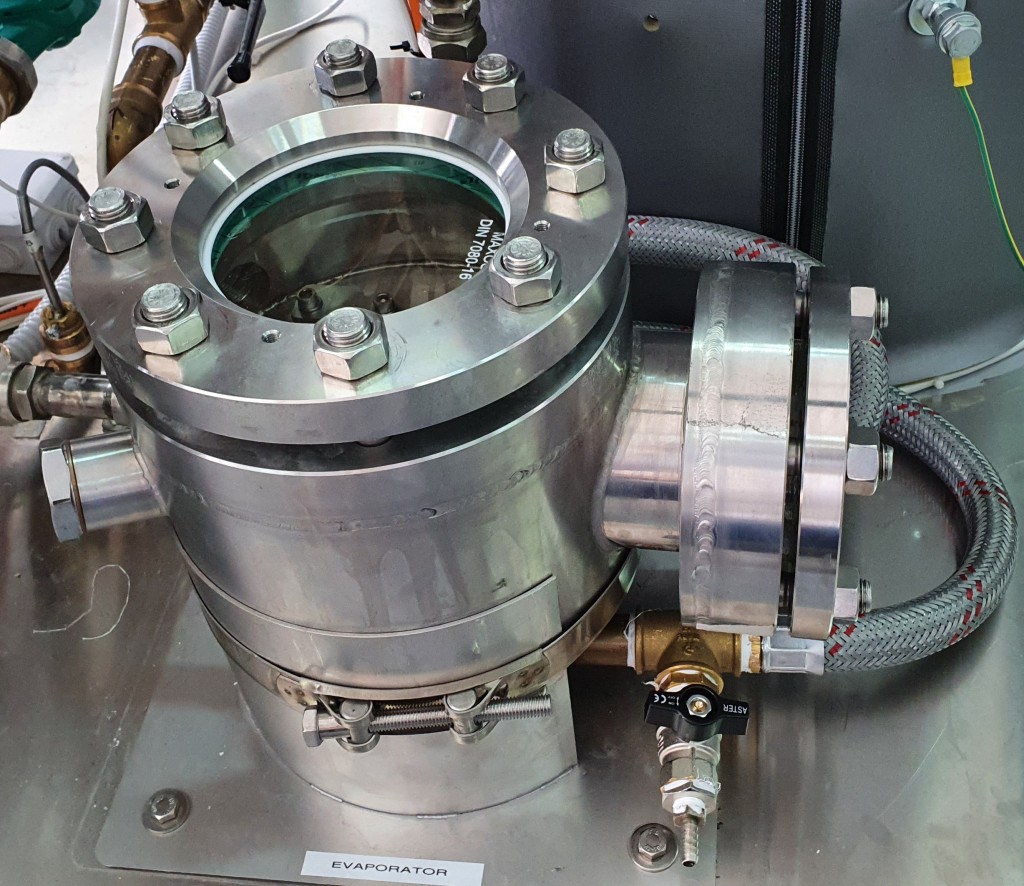
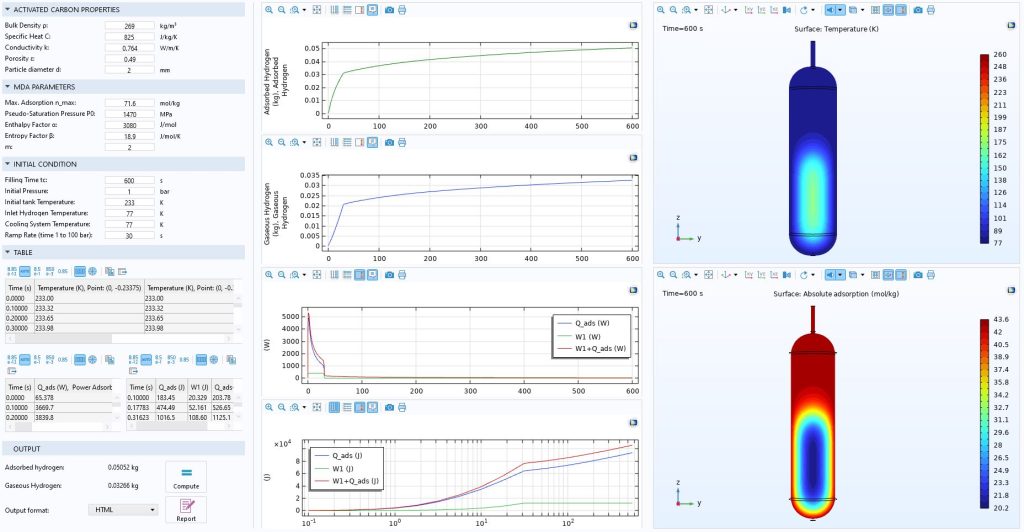
Air source heat pump based on the reverse Brayton cycle that transfers heat using air as the working fluid.
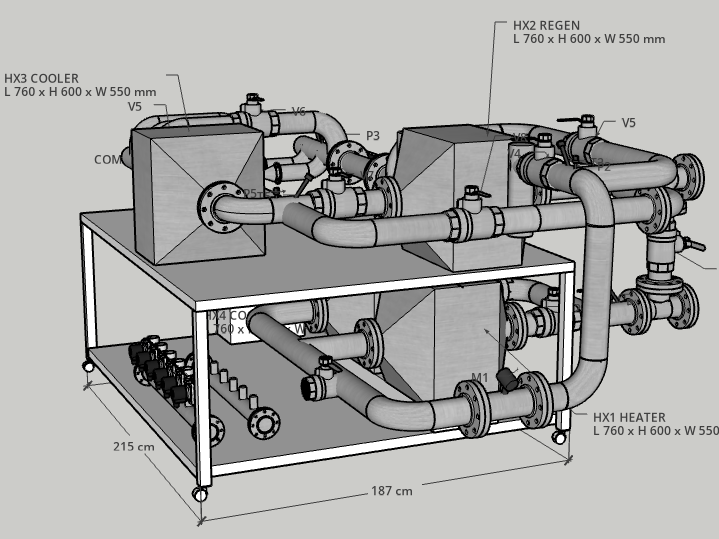
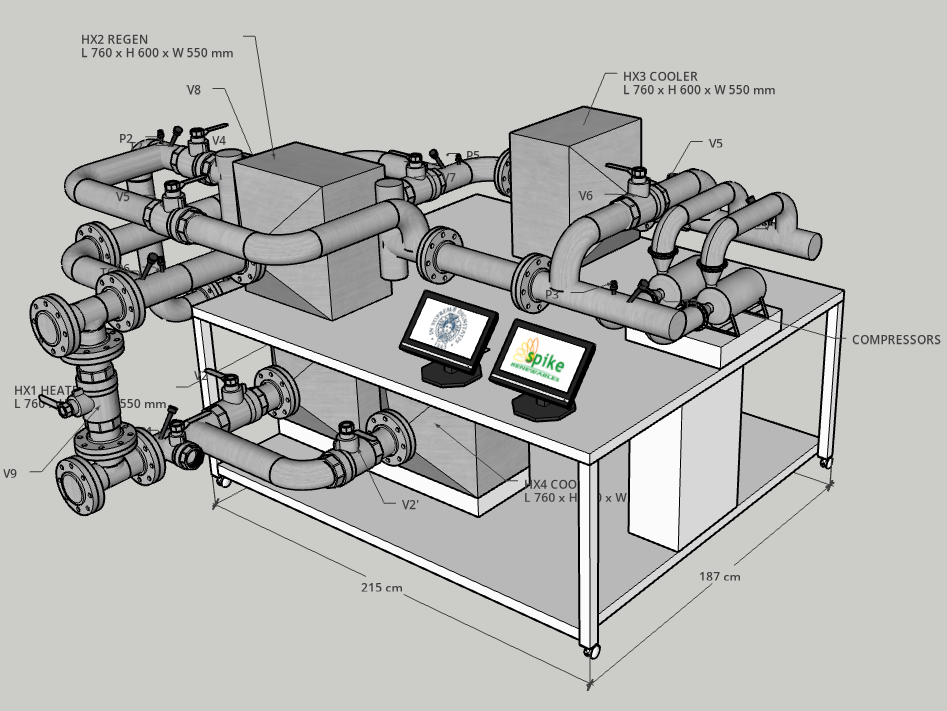
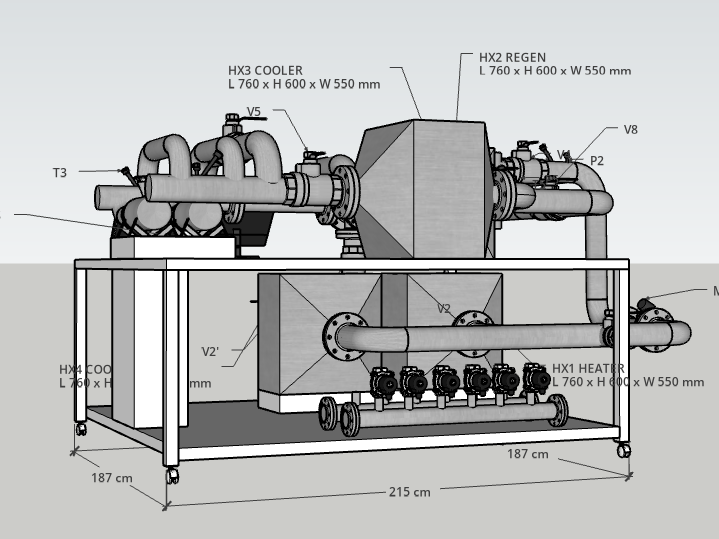
In an air source heat pump using the reverse Brayton cycle:
- Heat is removed from the cold outside air during the isobar heating phase and transferred inside the building.
- In the isobar cooling phase, the compressed warm air releases heat into the room to be heated.
The cycle can also be reversed to obtain a cooling effect: in this case, heat is removed from the indoor environment and released to the outside.
- Advantages: The reverse Brayton cycle uses air as the working fluid, avoiding chemical refrigerants that can be harmful to the environment. It can be particularly efficient when you want to take advantage of differences in outside air temperature.
- Disadvantages: The cycle requires compressors and turbines for expansion, which can be more complex and expensive than traditional heat pumps that use the vapor compression cycle. In addition, the cycle efficiency may be lower than that of heat pumps based on the Carnot or Rankine cycle.